Phishing attacks have evolved over the years from ridiculously obvious to extremely sophisticated.
It’s been nearly 20 years since the Nigerian Prince scam arose. If only we had provided a small cash advance or bank account information to complete the wire transfer, we could have had millions of dollars unclaimed in a Western Union account he was willing to give us.
Today, attackers use political events, health crises, religious campaigns, romantic connections, governmental threats, fake Zoom meetings, fake job postings, and multiple other methods. These attacks are all designed to get us to provide information or finances we would normally never provide.
The public and private sectors have developed security awareness campaigns to educate employees and reduce the risk of these attacks. However, as one method becomes known, another new, creative, and slightly more malicious method arises to circumvent controls and negate some of the education on those attack methods.
Today, there needs to be constant learning and education on the latest tools and techniques used to attack an organization or individual. Sometimes that education needs to train people to think like malicious attackers to understand how an attack could occur.
This blog post will walk you through the steps of a cyberattack that could cause you or a coworker to click on a malicious link or attachment, creating a major data breach. We’ll start with the phases in which such an attack could occur, using Human Resources as our example.
Read our blog post, “How Can Generative AI Be Used in Cybersecurity?”
4 phases of a cyberattack
Phase one: planning/reconnaissance: In phase one, a malicious attacker researches a target company’s job posting for positions and skills required.
Phase two: preparation: A malicious attacker then creates a fictitious resume, profile, references, and photo on common job sites to create an exact match of skills to the position and replicates profile(s) on common social media sites to head off any cross-checking efforts.
Phase two: attack: A malicious attacker applies to the target company website and lures the company to contact the attacker through what appears to be an exact match of skills. So rather than going after the fish, you set the bait for the “phish” to swim anxiously toward you.
Next, the HR rep contacts the malicious attacker’s phone (often a burner or disposable phone), hears a voice, and talks with the attacker about the position. The attacker has already researched and rehearsed the correct responses that the HR rep wants to hear.
Then, the HR rep requests the malicious attacker send a copy of their resume, which the attacker sends from a fictitious email address.
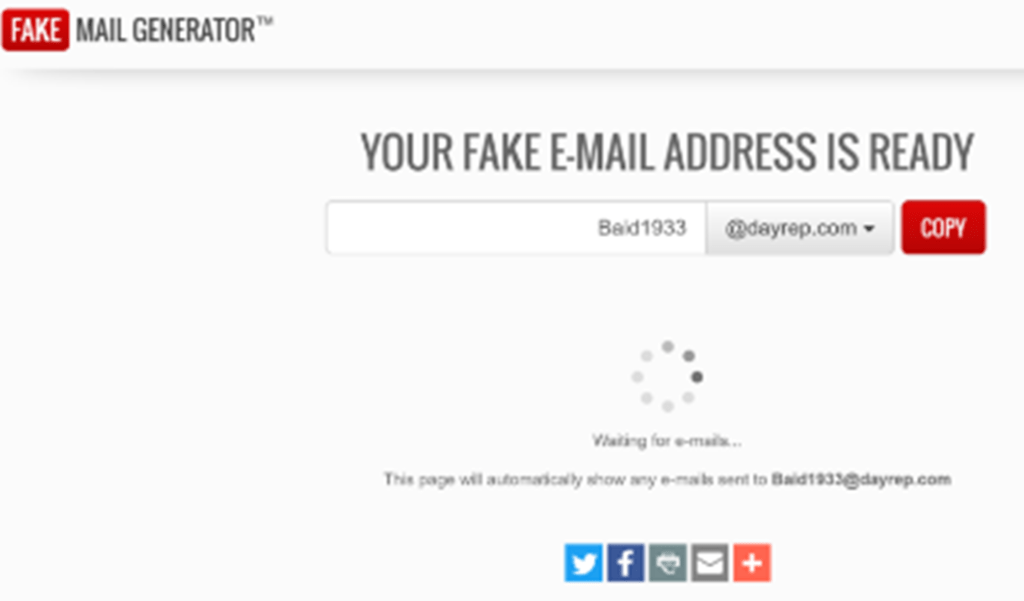
The HR rep receives an email with the fictitious name of the attacker (let’s use Jane Baid in this scenario) sent from the fictitious email address of the attacker ([email protected]) with the title of: “Jane Baid” Engineering Lead – Attached resume and social media reference.”
The HR rep feels a sense of trust based on the previous phone conversation and a short note from the attacker stating:
Dear (HR Rep Name),
I really enjoyed our conversation and have attached both my resume and link to my social media account as a further reference. Please let me know if you need any further information, and I look forward to speaking with you soon about the Engineering Lead position at (target company name).
Sincerely,
Jane Baid (Malicious actor’s fictitious name)
000-000-0000 – Malicious actor’s phone number from their burner or disposable phone
Phase four: acquisition. The HR rep, eager to pursue this promising candidate, has quickly clicked on the malicious attachment, which has now loaded sophisticated spyware that still appears like a resume to not arouse suspicion.
The HR rep also clicks on the malicious link containing malware that may go undetected and may also:
- Send credentials and other information to the attacker
- Harvest the contact list and send malicious links to those contacts
- Provide the attacker with unrestricted access to the HR rep’s device(s)
Spotting a cyberattack
Although this cyberattack was muti-phased and highly sophisticated, you can still identify the signs of malicious intent if you look hard enough. Here’s how.
- Hover over all links from [email protected].
- Notice differences between what you think the link represents and where it may lead you.
- Notice differences in domain names “Facebook1, Faceboook, T2witter.”
- Trust but verify.
- Unfortunately, things are not always the way they appear.
- Ensure you can validate multiple sources of information (education, criminal history, credit checks, contacts, name, address, phone number) before initiating any document/correspondence exchange. Although some information can be falsified, you can detect most discrepancies with enough prior validation.
- Malicious attackers use multiple methods to get people to click on a link or attachment or provide information they would normally not provide.
- You should not trust what may appear legitimate until you have sufficiently validated information.
- Conduct security awareness training and phishing simulation attacks of increasing sophistication and maliciousness.
- Sometimes the tightest administrative and technical controls will not replace the basic human factor and motivators such as trust, greed, embarrassment, boredom, loneliness, addictions, and fear. We need to train people to be aware of these tactics and how to react when these attacks arise.
Best way to protect against cyberattacks
Having read this blog post, you may be several steps closer to protecting your organization from some of the more sophisticated, exceptionally malicious, multi-phased phishing attacks than you were 10 minutes ago before you read it.
However, there’s more.
One of the best ways to combat the most sophisticated phishing attacks, in addition to policy and technical controls, is to continuously and proactively learn about the latest phishing methods and educate yourself — and encourage your organization to pursue education — on how to recognize, react, and report.
Learn more about how PCI handles cybersecurity and request a slide deck from our webinar, “Evolving Cybersecurity Threats & Challenges to Public Power.” Request the slide deck here.