Since the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) e-tags were constituted as a requirement for interchange scheduling, there’s been no innovation or development of tagging software to fulfill evolving clients’ needs.
e-Tag+ aims to change this.
We’ve been actively engaged with our clients to understand their evolving tagging requirements and built automated processes to facilitate their day-to-day activities. The automation requires the integration of several e-Tag+ services together with the PCI Platform. These services enhanced the application to be way more than just tagging software.
In this blog post, we’ll walk you through each service and the role they play in our processes.
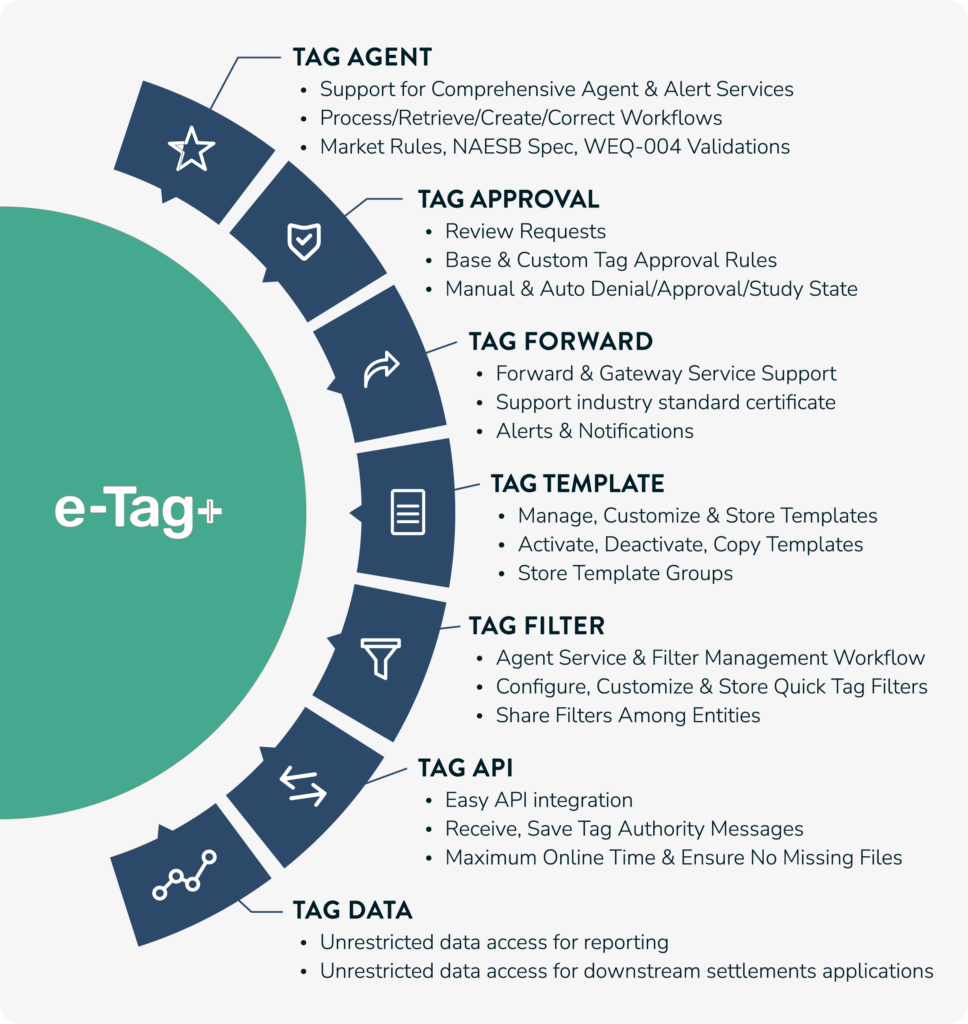
Tag Agent: This bridge allows communication between the e-tag Authority and PCI. It’s used for receiving/submitting tags and subsequent requests. The tag agent was the first service we improved to have automation capabilities. The automation allows the system to create tags from templates using any frequency provided by the client (sub-hourly, hourly, daily, monthly, etc.). Subsequently, the application picks up those newly created tags and validates and submits them. To guarantee our clients that the automated requests are correct, our validation engine rule ensures they fulfill timing rules from the North American Energy Standards Board (NAESB) and Wholesale Electric Quadrant (WEQ). We have also incorporated a direct interface with OASIS to retrieve transmission reservation data. Therefore, we can validate that the transmission profile in the tag is entitled to be submitted as well.
Tag approval: Every tag or request in which the client is an active participant in the transaction must be approved or denied. This is an overkill manual process for clients with a large tag volume. This process is also automated with e-Tag+. The clients configure custom rules for the users’ business criteria and scan every request returning an approval action. The process goes one step further and automatically submits the suggestions to the e-tag Authority, leaving the user interaction with approving tags down to the minimum.
Tag forwarding: This is the real-time chain forwarding of large volumes of tag data to third-party applications, including in-house apps such as data warehouse or back-office systems, other tag agents, and the PCI Platform.
Tag template: e-Tag+ is the only software on the market that allows users to store profiles in their templates with every single attribute required in a tag, including miscellaneous information, contracts, losses, etc. That’s how the app can create tags automatically.
Tag filter: A flexible combination of tag attributes creates custom filters. One use of these filters is to return sets of tags that can be automatically adjusted with other data sources.
Tag API: e-Tag+ back-end APIs are exposed and easy to integrate with the PCI Platform or any other software application.
The automated workflows we offer have already been deployed and delivered to several customers in the production systems. The diagram below shows some of the most outstanding processes.
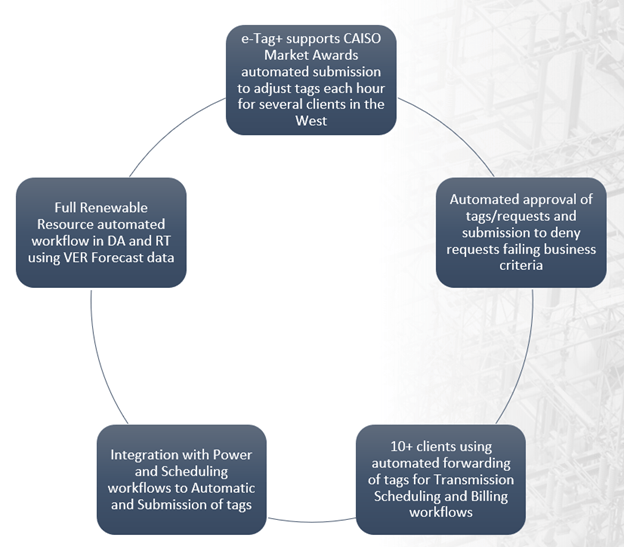
Renewable generation resource automated workflow
Clover Creek is a solar generation resource that Utah Municipal Power Agency (UMPA) transacts with Pacificorp (PAC). The day-ahead workflow submits every 15 minutes before-the-fact adjustments to tags and base schedules to the Base Schedule Aggregation Portal (BSAP) for seven days in the future.
Figure 1 shows the flow diagram of every step involved in the workflow
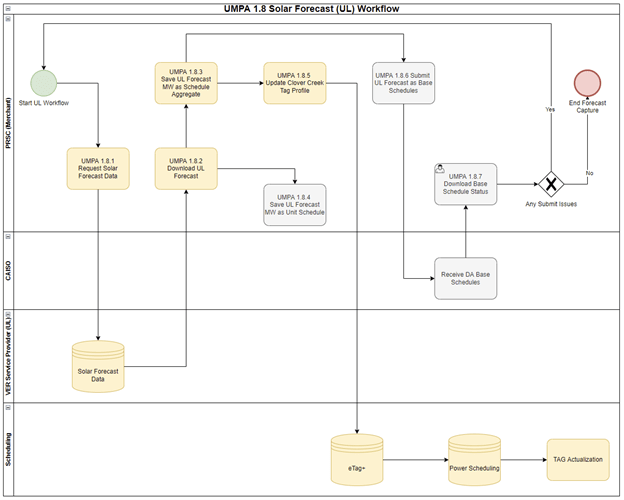
To automate this workflow for the user, we start by having daily tags for the next seven days already created in the system. e-Tag+ creates the tags using the Clover Creek template stored in the system. On the PCI Platform side, a scheduled task running every 15 minutes starting from the top of the hour requests forecast data to UL and stores it for further submission to e-Tag+ and BSAP.
Once the data is downloaded, the task triggers two processes in parallel:
- Profile change adjustment: The PCI Platform calls the e-Tag+ app to return available tags. It uses custom filters to guarantee that only one tag is returned daily. Then it executes validation of the tag adjustments for the seven tags. The process submits the requests and forwards the approval and new profile back to the PCI Platform for automatic actualization of the schedule. Users can review the tag audit to verify requests submitted from the Generation Supply Management System (GSMS) and the trend of the forecast changes per request (Figure 2).
- Base schedules submission: The task submits the base schedules to BSAP, downloads the values, and displays those in the DA position screen.
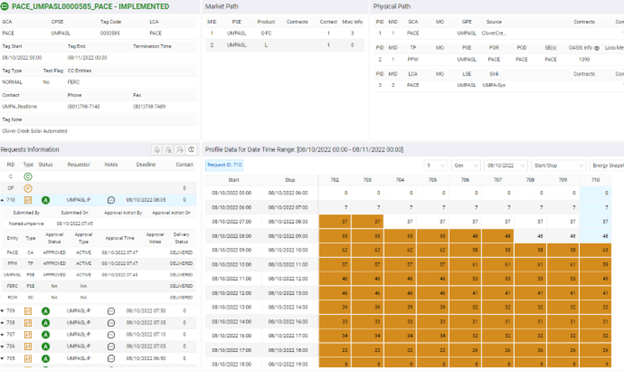
Automating this process has saved clients significant time (they used to even have shifts at night to update the tag).
We’re committed to understanding our clients’ e-tagging challenges and refining e-Tag+ to address their evolving needs.
Visit our e-Tag+ product page to learn more about how e-Tag+ can save your team time and give them the answers they need.







