Established in 1970, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) has the same mission as every other Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) and Independent System Operator (ISO) in the U.S.: As an independent non-profit organization, it’s charged with overseeing the reliable transmission of electricity across its grid, including the management of ERCOT hubs.
But just like good Texas barbecue, the Lone Star State has its own way of accomplishing this mission, and it’s a very different approach from what you’ll find in CAISO, NYISO, PJM, or the other ISO/RTOs.
Understanding ERCOT’s distinct methods is crucial not only for grasping how Texas maintains its energy independence but also for recognizing the implications of this approach on market operations, grid reliability, and renewable energy integration. This knowledge can provide valuable insights for energy professionals, policymakers, and anyone interested in the future of energy management in Texas.
ISO/RTO Documentation Chatbot
Use our AI to search Business Practice Manuals from ISO/RTO markets at no cost.
The Lone Star State goes it alone
Like its counterparts, ERCOT operates both day-ahead and real-time energy markets, but unlike other ISOs/RTOs in North America, its power grid has minimal connections with other states. This creates an energy island not subject to federal jurisdiction or regulation by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). Rather, ERCOT’s network of 1,250 generation units and 54,100 miles of transmission lines is solely responsible for providing power to roughly 90% of the state, as shown in Figure 1.
Established in 1970, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) has the same mission as every other Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) and Independent System Operator (ISO) in the U.S.: As an independent non-profit organization, it’s charged with overseeing the reliable transmission of electricity across its grid, including the management of ERCOT hubs.
But just like good Texas barbecue, the Lone Star State has its own way of accomplishing this mission, and it’s a very different approach from what you’ll find in CAISO, NYISO, PJM, or the other ISO/RTOs.
Understanding ERCOT’s distinct methods is crucial not only for grasping how Texas maintains its energy independence but also for recognizing the implications of this approach on market operations, grid reliability, and renewable energy integration. This knowledge can provide valuable insights for energy professionals, policymakers, and anyone interested in the future of energy management in Texas.
The Lone Star State goes it alone
Like its counterparts, ERCOT operates both day-ahead and real-time energy markets, but unlike other ISOs/RTOs in North America, its power grid has minimal connections with other states. This creates an energy island not subject to federal jurisdiction or regulation by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). Rather, ERCOT’s network of 1,250 generation units and 54,100 miles of transmission lines is solely responsible for providing power to roughly 90% of the state, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: ERCOT County Map (Source: ERCOT)
We saw the downside of this limited interconnection capacity during 2021’s Winter Storm Uri when extremely cold temperatures led to widespread outages. Without the infrastructure to import power from other states, nearly 69% of the ERCOT’s 26 million customers lost power at some point during the storm.
ERCOT’s approach to electricity transmission is considered by many to be emblematic of the state’s independent spirit, but it also has several advantages. Most notably, the state is one of the top producers and consumers of renewable energy. A 2023 study found that Texas generated more renewable energy than any other state — and nearly 55% more than California, which came in second. Texas also ranked second for battery storage capacity, with 2.09 GW in 2022. That the state has increased the adoption of wind, solar, and battery storage at such levels in recent years is attributed to the isolated nature of its grid.
ERCOT hub vs. load zone
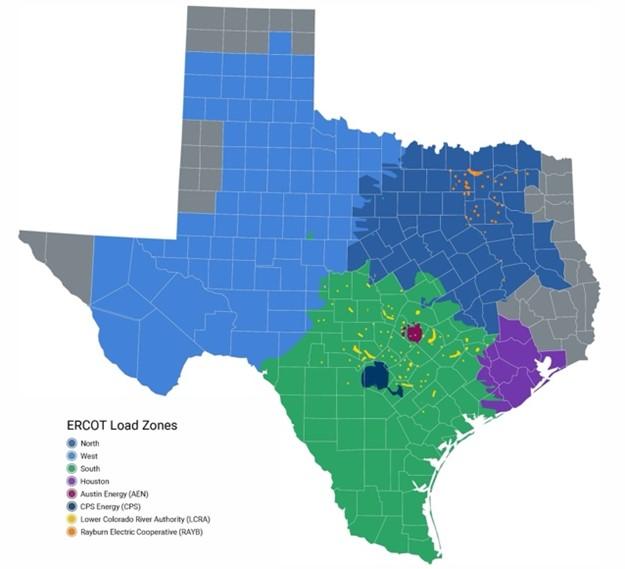
Figure 2: ERCOT hubs and load zones map (Source: ERCOT)
ERCOT hubs and load zones are integral parts of the electricity market in Texas, but they serve two different purposes. The state is broken down into north, south, Houston, and west regions. ERCOT also uses hubs to support electricity trading and risk management, while ERCOT load zones are used mainly for load pricing and settlements. (See ERCOT hubs and load zones map in Figure 2.)
ERCOT hubs

Hubs are made up of one or more Electrical Buses, which are used in calculating DAM and RTM HUB prices.
ERCOT trading hubs enable the trading of electricity within the state by aggregating and averaging pricing points from multiple nodes across the hub. ERCOT computes LMPs for six hubs: North, South, Houston, West, Average ERCOT Hub, and Average Bus Hub. This provides the market with a standardized pricing reference for each hub, streamlining electricity transactions and settlements and giving market participants the ability to hedge against price volatility.
ERCOT load zones

ERCOT load zones, on the other hand, represent specific geographic areas where electricity is consumed. Each zone has multiple nodes that measure local demand; load zone pricing reflects actual locational marginal prices based on local conditions. ERCOT models three types of load zones:
- 4 competitive load zones: North, South, West, Houston
- 4 load zones for Non-Opt-in Entities (NOIEs): CPS, LCRA, Austin, RAYBN
- 5 DC load zones
In other words, the load zones help manage grid congestion and identify where electricity is needed and the cost of delivery to those areas. Understanding the intricacies of ERCOT load zones is essential for effective market participation and grid management. With the complexity and unique challenges of the ERCOT market, having the right tools to navigate and optimize these aspects is crucial.
PCI Energy Solutions offers an enterprise software suite designed to enhance your participation in the ERCOT market, ensuring efficient operations and accurate settlements. Contact us to learn more about how we can support your energy management needs.







